Tools and Softwares
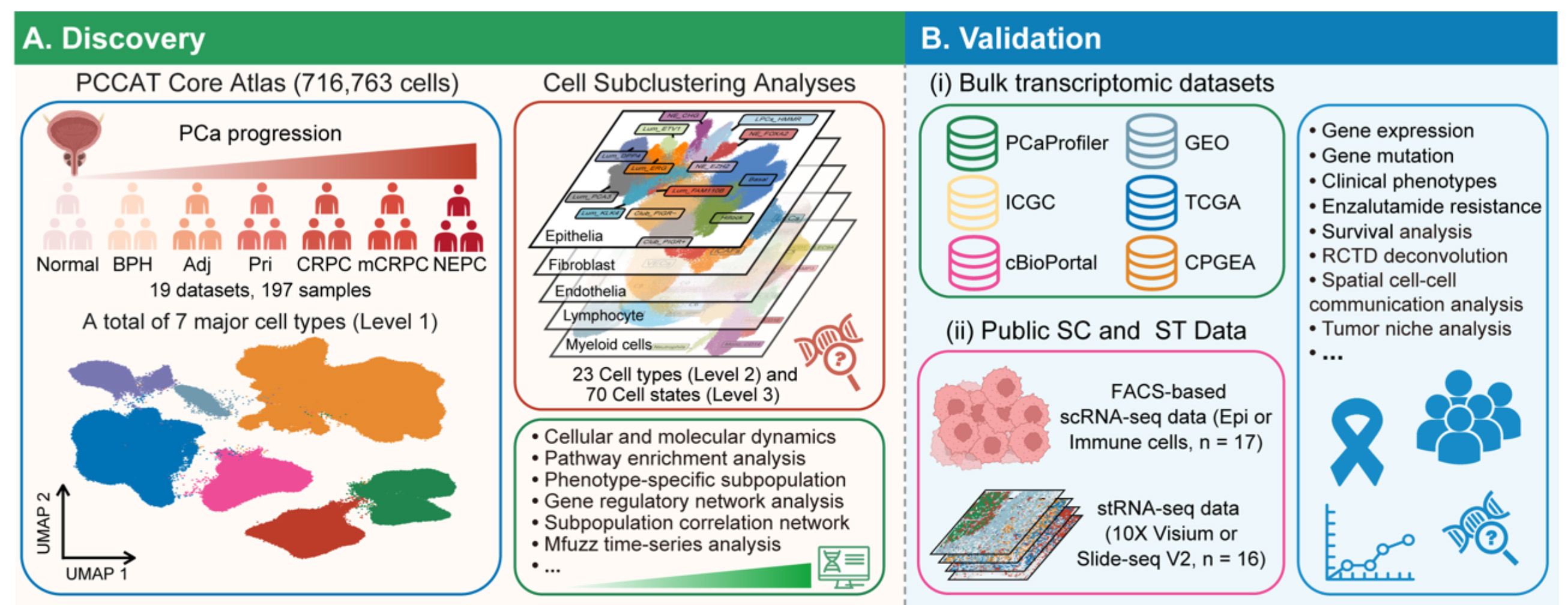
- Prostate Cancer Cell Atlas (PCCAT):
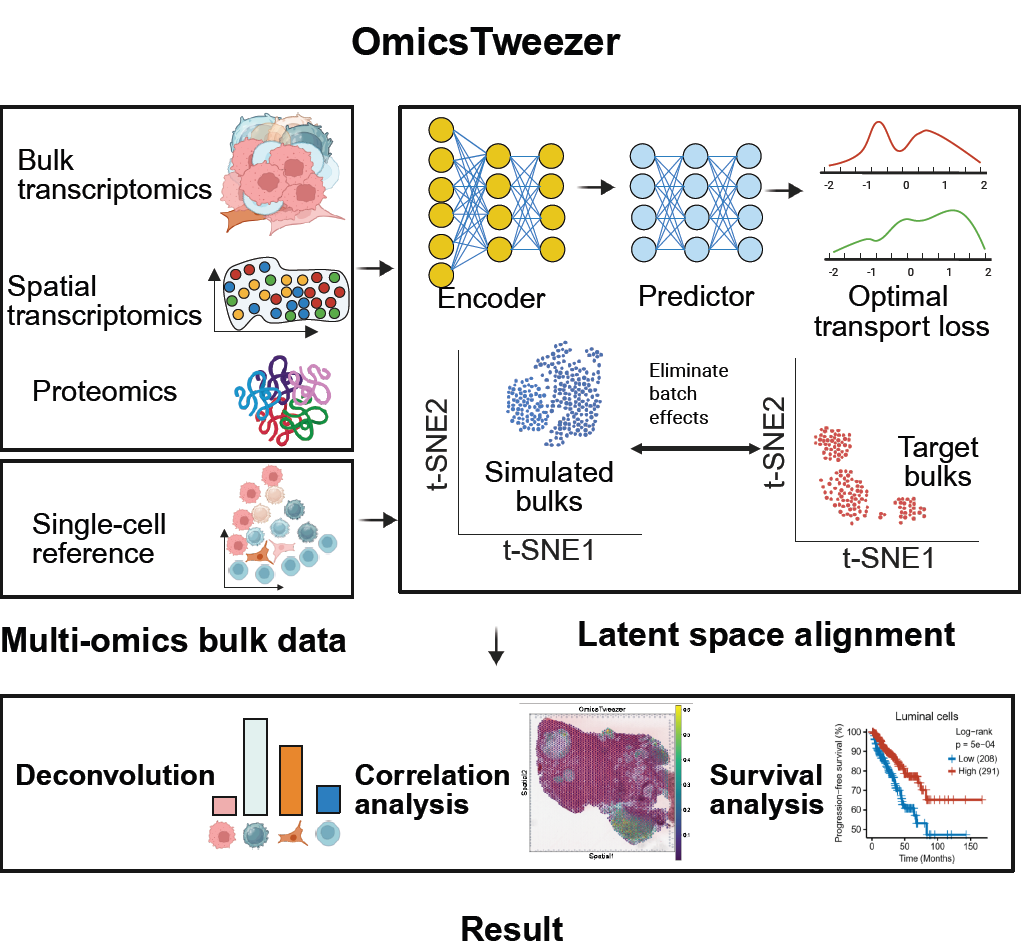
Deciphering single-cell heterogeneity and cellular ecosystem dynamics during prostate cancer progression, Zhao et al., bioRxiv, 2024 - OmicsTweezer: a unified framework for the deconvolution of bulk RNA-seq, proteomics, and low-resolution spatial omics.
OmicsTweezer:a data distribution-independent cell deconvolution model for multi-omics data, Yang et al., Cell Genomics, 2025 - PhAre:
(Ph)ysiology (A)ge P(re)diction: Like tree rings, time carves messages in our blood, but not always evenly.
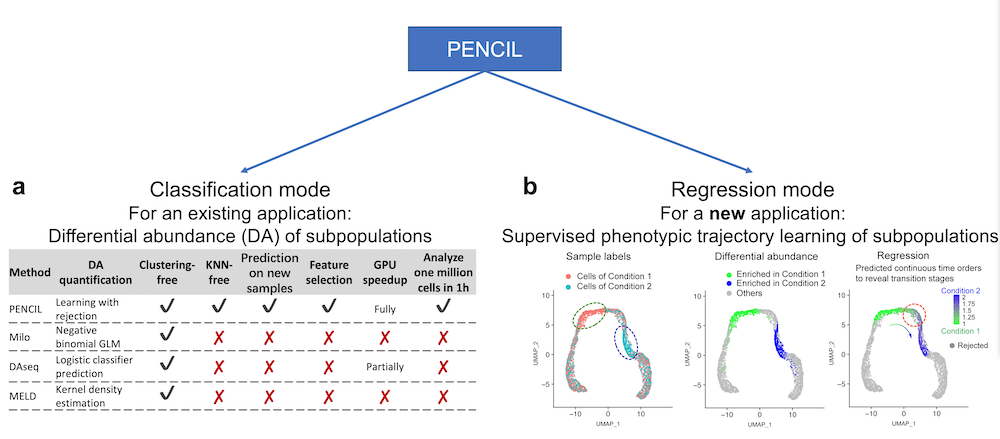
Biologically informed machine learning modeling of immune cells to reveal physiological and pathological aging process, Zhang et al., Immunity & Ageing, 2024 - PENCIL: Supervised learning of high-confidence phenotypic subpopulations from single-cell data, Ren et al., Nature Machine Intelligence, 2023
- SCISSOR: Single-Cell Identification of Subpopulations with bulk Sample phenOtype coRrelation
Identifying phenotype-associated subpopulations by integrating bulk and single-cell sequencing data, Sun et al., Nature Biotechnology, 2022 - DaPars: Dynamic analysis of Alternative PolyAdenylation from RNA-seq, Xia et al., Nature Communications, 2014
- NSMAP: A Method for Spliced Isoforms Identification and Quantification from RNA-Seq, Xia et al., BMC Bioinformatics, 2011
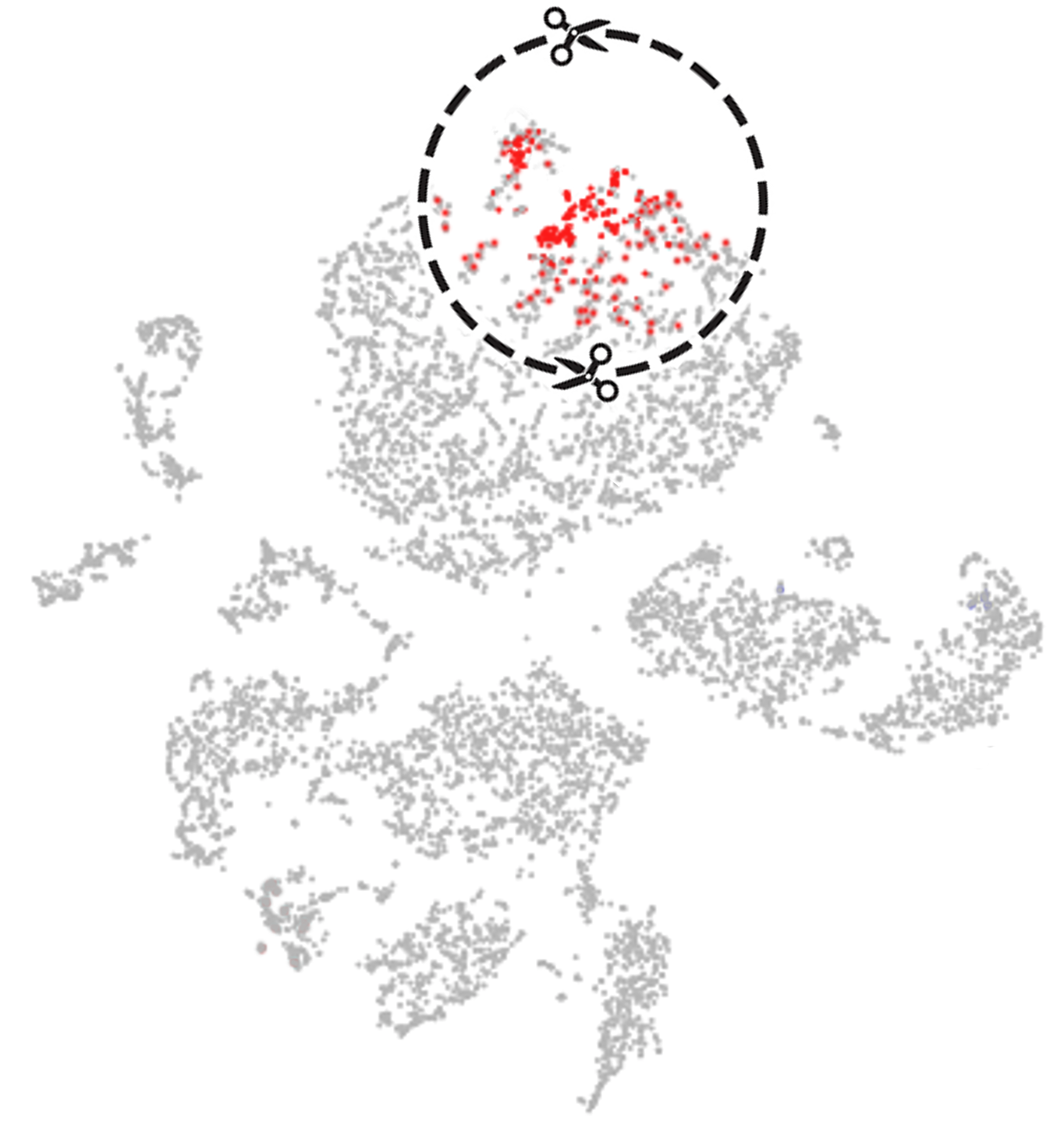
The goal of Scissor is not to annotate each cluster of cell population but to identify the cell subpopulations that are most highly correlated with the specific phenotypes which are widely availabe in bulk sequencing.
The rationale of our analysis is based on a Buddhist theory that “Any individual can only drink ONE bottle of water from an entire river.”